Photoluminescent sensor for acetylcholinesterase inhibitor determination†
Abstract
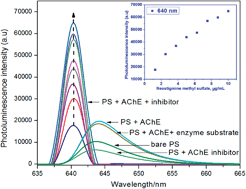
An acetylcholinesterase immobilized p-type porous silicon material for sensing acetylcholinesterase inhibitors was demonstrated. The enzyme immobilized photoluminescence surface upon incubation with standard acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (neostigmine methyl sulfate and tacrine) for 30 minutes at 37 °C triggers the photoluminescence with up to a 3 fold enhancement in the intensity with a hypsochromic shift of 3 nm. The dramatic change in photoluminescence of the enzyme immobilized surface upon reaction with the enzyme inhibitor can be used as a tool for the detection of acetylcholinesterase inhibitors by utilizing the subsequent photoluminescence response after the incubation with the corresponding inhibitor drug.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...