A study on effects of naphthalimide derivative-capped quantum dots on the cellular internalization, proliferation, and apoptosis ability†
Abstract
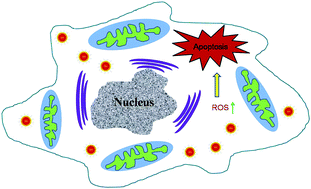
Quantum dots (QDs) have shown great potential in monitoring and imaging cancer cells because of their unique photochemical and photophysical properties. However, it is little-known whether QDs affect the cellular internalization, proliferation and apoptosis. Here a new class of multifunctional QDs capped with ligands that possess L-Lys or L-Arg and naphthalimide (NI), linked by carboxyl groups (L-Lys-NI@QDs and L-Arg-NI@QDs, respectively), have been synthesized. We found that these QDs are of controllable sizes, in the range of 4 to 5 nm and have strong optical emission properties. The cellular uptake of NI derivative-capped QDs was monitored by flow cytometry and confocal microscopy. The results of in vitro cytotoxicity revealed that NI derivative-capped QDs, with better cell selectivity, could inhibit the growth of multiple cancer cells more potently than amonafide. They effectively inhibited the proliferation of cells due to apoptosis, which was confirmed by Hoechst 33342, annexin V-FITC and JC-1 staining and mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) experiments. The most potent NI derivative-capped QDs, L-Arg-NI@CdSe/ZnS, were verified to efficiently induce apoptosis via a reactive oxygen species (ROS) mediating mitochondrial dysfunction, and were more effective in promoting programmed cell death in HepG2 cells in a preliminary mechanistic study.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...