Synthesis of an acid-cleavable and fluorescent amphiphilic block copolymer as a combined delivery vector of DNA and doxorubicin
Abstract
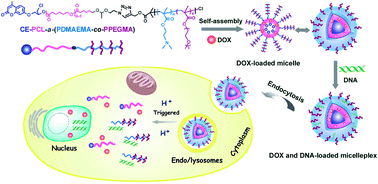
An emerging strategy for synergistic gene and drug therapy is establishing a new paradigm for the synthesis of diversified and functional block copolymers with applications ranging from gene and drug delivery to fluorescence detection. In this paper, we report on a novel amphiphilic block copolymer containing a fluorescent coumarin derivative (CE), an acid-cleavable (acetal group, -a-) linkage between hydrophobic poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL) and hydrophilic poly[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate] (PDMAEMA) and poly[poly(ethylene glycol)methyl ether methacrylate] (PPEGMA) blocks, abbreviated as CE-PCL-a-(PDMAEMA-co-PPEGMA), which was synthesized by a combination of atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP), ring-opening polymerization (ROP) and CuAAC “click” reaction. The chemical composition and structures of these copolymers were fully characterized by 1H NMR and FT-IR analyses, while the molecular weights and molecular weight distributions were measured by gel permeation chromatography (GPC). The micelles self-assembled from these block copolymers could simultaneously encapsulate anti-cancer drug doxorubicin (DOX) and DNA to form a micelleplex with the hydrophilic brush-type PPEGMA on the surface, and the loaded cargoes could be released after the acetal linkage was cleaved under intracellular acidic conditions. Subsequently, the formed micelles as the drug and gene co-delivery vectors were investigated by employing gel retardation assay, zeta potential, dynamic light scattering (DLS), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). A fluorescence spectrometer was further used to evaluate the fluorescence of polymers. Finally, in vitro drug release, cytotoxicity and transfection were also studied. All these results indicated that this acid-cleavable and fluorescent block copolymer would hold significant potential as a combined drug and DNA carrier.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...