A novel nanoassembled doxorubicin prodrug with a high drug loading for anticancer drug delivery†
Abstract
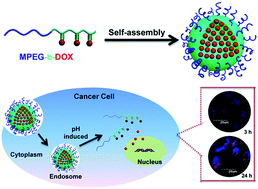
We report here a novel doxorubicin (DOX) prodrug that reduces the proportion of inactive materials and minimizes drug leak. In aqueous solutions, the resulting DOX prodrug could spontaneously form stable micelles with diameters of ∼80 nm with a DOX loading content as high as ∼40 wt%. The subsequent cytotoxicity and cell internalization behavior indicated that the resulting prodrug could show a high in vitro anticancer efficacy. We believe that this strategy could be developed to design prodrugs of various anticancer drugs and thus offer new prodrugs for cancer therapy.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...