Synthesis of a phenylalanine imprinted polymer for attenuation of phenylalanine absorption via the gut in a murine hyperphenylalaninemia model
Abstract
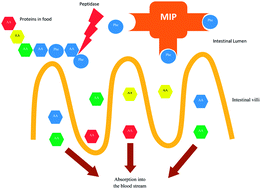
Polymer technology plays an influential role in biomedical sciences. Molecular imprinting is a technique for preparation of polymers with structure-selective adsorptive properties. High selectivities of these materials have nowadays advanced to the point that they are being utilized for several biomedical applications such as drug delivery. Phenylketonuria is a genetic disease characterized by accumulation of phenylalanine (Phe) in blood with toxic consequences. The aim of the present study is to synthesize a phenylalanine imprinted polymer for attenuation of phenylalanine absorption in the gut in a murine hyperphenylalaninemia model. A molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) against Phe and a non-imprinted polymer (NIP) were synthesized and their Phe binding properties were studied in Simulated Intestinal Fluid (SIF). Two classes of binding sites were then found in the MIP: high affinity (KD = 62.5 μM) and low affinity (KD = 1 mM). Histological toxicity and LD50 of the MIP, after oral administration to murine hyperphenylalaninemia, were examined prior to investigation of the effects of the imprinted polymer on blood Phe concentrations in animal models. Our findings suggest that the MIP against Phe can decrease the blood Phe concentration in an animal model of hyperphenylalaninemia.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...