Calcium phosphate neuron-like structures: a rare case or a common structure?
Abstract
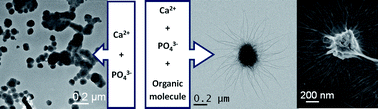
Underneath the unique and beautiful structures of biominerals there is always the presence of organic molecules that tightly interact with the developing inorganic nuclei/crystal directing its growth and assembly towards the final structure. This close interdigitation between organic and inorganic matter renders biominerals not only unique in their appearance but also with exceptional properties. A notable case of such combination is observed when combining double hydrophilic block copolymers (DHBCs) with different ions. In the particular case of calcium phosphate systems, the incorporation of DHBCs was found to induce the formation of unique and delicate neuron-like structures. The present article highlights that such structures are more common than probably expected and they can be created using much simpler organic molecules of a wider nature such as non-ionic surfactants (Tween 80 or Span 20), anionic polymers (sodium polyacrylate) and cationic polymers (polydiallyldimethylammonium chloride). The reaction conditions are however crucial in the stabilization of the structures.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...