The influence of fluorocarbon chain and phosphorylcholine on the improvement of hemocompatibility: a comparative study in polyurethanes†
Abstract
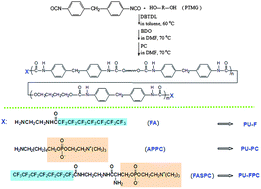
To study the influence of fluorinated surfaces and biomimetic surfaces on the improvement of the blood compatibility of polymers, three monomers containing a fluorinated tail and/or phosphorylcholine groups were designed and synthesized, and were then introduced into polyurethanes based on 4,4′-diphenylmethane diisocyanate (MDI), poly(tetramethylene glycol) (PTMG) and 1,4-butanediol (BDO) via end-capping. The bulk and surface characterization of the polyurethanes was carried out by dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic analysis (XPS), atomic force microscope (AFM), and water contact angle measurements. The results indicate that the fluorocarbon chains can drive the phosphorylcholine groups to aggregate at the surface of polyurethane, and the two components show spontaneous arrangement to adapt to the environment when in contact with water. The preliminary evaluation of hemocompatibility was carried out via fibrinogen adsorption and platelet adhesion. The fluorocarbon chains and phosphorylcholine groups showed a synergistic effect on the improvement of hemocompatibility.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...