A high efficiency H2S gas sensor material: paper like Fe2O3/graphene nanosheets and structural alignment dependency of device efficiency†
Abstract
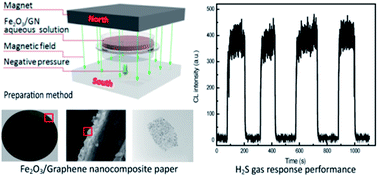
Fe2O3/graphene was synthesized successfully by a super critical CO2-assisted thermal method and further made into paper-like nanosheets by directed-flow, vertical assembly of individual Fe2O3/graphene nanosheets under a controlled magnetic field. Characterization of the samples was carried out by both electron microscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The sensor materials outperform many other paper-like materials for H2S gas detection. In addition, vertically and horizontally aligned nanosheets were used as sensing materials to detect H2S gas along with chemiluminescence measurements. Importantly, the nanoscale Fe2O3/graphene sheets with the vertical arrangement are more beneficial than the nanosheets with the horizontal arrangement in terms of sensitivity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...