Electrochemically stable cathode current collectors for rechargeable magnesium batteries
Abstract
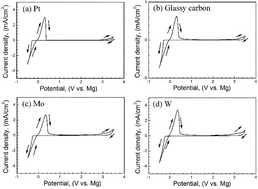
Rechargeable magnesium (Mg) batteries are attractive energy storage systems that could yield cost-effective energy solutions. Currently, however, no practical cathode current collector that can withstand more than 2.0 V in Mg2+ electrolytes has been identified; this greatly hinders cathode research. Here we identified that molybdenum (Mo) and tungsten (W) are electrochemically stable (>2.8 V) through formation of passive surface layers. The presented results could have a significant impact on the development of high voltage Mg batteries.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...