Synthesis and characterization of pure P2- and O3-Na2/3Fe2/3Mn1/3O2 as cathode materials for Na ion batteries
Abstract
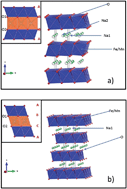
The solid state synthesis and electrochemical characterization of pure P2- and O3-Na2/3Fe2/3Mn1/3O2 have been carried out. Both phases have been characterized with XRD, solid state NMR, and ICP techniques. The initial charge capacity of the P2-phase reached 114.7 mA h g−1 and was followed by a discharge capacity of 151.09 mA h g−1 within the voltage range of 4.2–1.5 V at C/10. The capacity retention gradually decreased to 122.83 mA h g−1 at the 10th cycle, and then remained stable up to the 15th cycle. The O3-phase resulted in a first charge capacity of 134.01 mA h g−1 with a discharge capacity of 157.47 mA h g−1 under the same experimental conditions. The capacity retention gradually decreased to 122.24 mA h g−1 at the 10th cycle but, as in the other polymorph, the capacity remained stable at least up to the 15th cycle. Although the voltage profile is slightly different, the overall electrochemical performance of both phases is shown to be very similar, which implies that, contrary to common belief, the electrochemical performance of this compound does not highly depend on the layer stacking sequence adopted by the material.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...