Multifunctional perovskite capping layers in hybrid solar cells†
Abstract
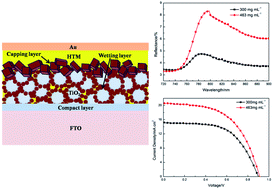
In this study, the crucial role of perovskites capping layers in the TiO2/CH3NH3PbI3 hybrid solar cells is investigated. The capping layers are realized by controlling the concentration of PbI2 solutions in the sequential deposition process. The morphologies of the active layers are studied by high-resolution scanning electron microscopy (HR-SEM). The amount of perovskites in capping layers increases with the concentration of PbI2 solution, and the coverage of perovskite capping layers on TiO2 films is better developed. Except for the correlation between photocurrents and coverages of perovskite proposed by Snaith, we revealed a more detailed relationship between the photovoltaic performances and perovskite capping layers. It is noteworthy that UV-vis absorption increased with perovskites in capping layers. Moreover, according to the diffuse reflection spectra, light scattering, which is beneficial for the conversion efficiency of photons to electrons by directly preventing most of the incident light from transmitting out, is also enhanced due to both the emergence of larger-size particles in the capping layers and the higher effective dielectric coefficient. All of the aforementioned aspects result in high photocurrents up to 20.6 mA cm−2. Efficiency as high as 10.3% is ultimately achieved by a simple control of PbI2 concentration in the sequential deposition process.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...