High surface area DPA-hematite for efficient detoxification of bisphenol A via peroxymonosulfate activation
Abstract
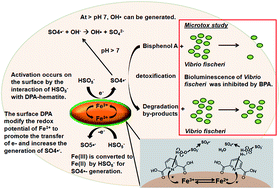
A novel dipicolinic acid-functionalized hematite (DPA-hematite) with high surface area was prepared by co-precipitation of a Fe(III)–DPA complex. It was used as a catalyst to activate peroxymonosulfate (PMS) for bisphenol A (BPA) detoxification. The XRD, FESEM, TEM and FTIR characterization indicated that nano-sized DPA-hematite with aggregated quasi-nanosphere morphology was obtained with a 1 : 1 ratio of Fe(III) to DPA. Higher catalytic activity of DPA-hematite over other Fe(III)-based catalysts was observed for BPA oxidation in the presence of oxone. The kinetics of BPA removal was investigated using a kinetic model with BPA concentration, initial oxone dosage and surface area of DPA-hematite. For the first time, the acute toxicity of BPA solution over time with elimination of oxone toxicity interference was studied using Vibrio fischeri bacteria and the results indicated that the evolution of acute toxicity was highly dependent on the initial oxone dosage. Under deficit oxone conditions, BPA was completely transformed to by-products along with decreased intrinsic toxicity but ring-opening reactions were barely observed which can be explained based on the dimerization–mineralization degradation pathways. Under excess oxone conditions, the intrinsic toxicity of BPA solution decreased along with ring-opening reactions leading to a greater extent of mineralization. The DPA-hematite can be reused for BPA detoxification for at least three cycles in the presence of 2.0 g L−1 oxone.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...