Optimised exfoliation conditions enhance isolation and solubility of grafted graphenes from graphite intercalation compounds†
Abstract
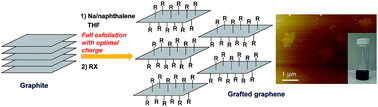
In bulk applications, it is essential that graphene sheets disperse individually in solvents or matrices, and therefore, suitable functionalisation regimes are crucially important. Here, isolated, highly soluble, alkyl-grafted graphenes were synthesised by reacting exfoliated Na-reduced graphite intercalation compounds (GIC) with alkyl halides. In this reaction, efficient exfoliation of the Na-reduced GICs into individually-dispersed negatively-charged graphenes provides accessible surface area for grafting. Increasing the alkyl chain length leads to large decrease of the grafting ratio (GR), demonstrating that steric factors also play an important role. However, optimising the Na concentration (C/Na ratio) in the reaction was very effective for improved exfoliation and increased GR. The X-ray diffraction measurements suggest that particular C/Na ratios (C/Na = ∼12) led to full exfoliation, by balancing total charge and charge condensation effects and that the GR can be significantly increased even in the case of long alkyl chains (eicosyl chains), corresponding to a high solubility of 37 μg ml−1 and high yield in o-dichlorobenzene. Moreover, the absolute Na concentration is the critical parameter, with the same optimum (∼0.01 M) for exfoliation and grafting of GIC at all graphite concentrations; it was possible to graft even at high graphite concentration (0.3 M (3.6 mg ml−1)) successfully.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...