Physical mixtures of CeO2 and zeolites as regenerable indoor air purifiers: adsorption and temperature dependent oxidation of VOC†
Abstract
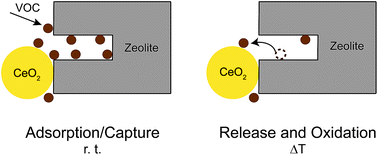
Removal of volatile organic compounds (VOC) and indoor air quality regulation through adsorbers required exchange or maintenance of active materials. In this work, we combine well known VOC adsorbers with oxidation catalysts as intimate particulate mixtures. We demonstrate how typical VOC can subsequently adsorb on such mixed material fixed beds (usually days to weeks; the common state of the system, adsorption phase) using small organic compounds (diethyl ether, triethylamine), monoterpenes such as linalool and limonene, and hexanoic acid. Occasional regeneration runs through heat up of the fixed bed results in simultaneous desorption and oxidation of the accumulated VOC, thus regenerating full adsorption capacity for a next adsorption phase. We investigated both small pore zeolites (H-ZSM-5) and larger pore zeolites (13X) and found a distinct interplay between the pore size and the type of VOC. Thermogravimetry coupled with mass spectroscopy was used to quantitatively study the effects of mixing composition and temperature on adsorber performance and regeneration. The here investigated bi-functional systems combine very low maintenance costs and materials requirement with low air flow and exchange costs, thus suggesting mixed (two-functional) bed adsorbers with catalytic function as sustainable alternatives to currently used single use systems based on granulated zeolites or activated carbon. In this work we show the ability of zeolite/cerium oxide physical mixtures to adsorb and capture different classes of VOC at room temperature and release them for oxidation at higher temperatures in a regenerative and sustainable process.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...