Nanostructured flexible Mg-modified LiMnPO4 matrix as high-rate cathode materials for Li-ion batteries†
Abstract
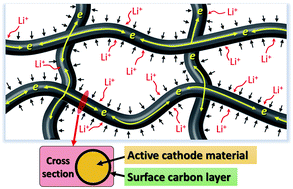
One-dimensional (1D) electrode materials have attracted much attention recently because of their potential application in flexible battery technology. Many 1D anode materials based on carbon and metal oxides have been synthesized for flexible batteries, however only limited studies on the cathode side have been conducted. Here, we report the synthesis of high-rate cathode electrodes based on Mg-modified LiMnPO4 nanofibers. The nanofibers are embedded inside a nanostructured conducting carbon matrix to enhance their electronic conductivity and structural integrity while retaining flexibility. As a result, a 50% increase in capacity is obtained, achieving an outstanding performance of 135 mA h g−1 at a C/10 rate (15 mA g−1). This nanostructured Mg-modified LiMnPO4 matrix also exhibited superior rate capability and much better cycleability compared to its LiMnPO4 counterpart. Even at a high charge/discharge rate of 5C (750 mA g−1), 80% of the capacity (107 mA h g−1) is still retained, representing, to the best of our knowledge, the best rate performance for LiMnPO4-based electrodes. More importantly, such a superior rate capability is achieved with an excellent cycleability (no capacity fading for 200 deep cycles).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...