Luminescent carbon nanoparticles: effects of chemical functionalization, and evaluation of Ag+ sensing properties†
Abstract
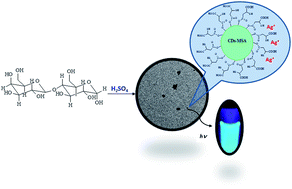
Luminescent carbon-based nanoparticles, addressed as carbon dots (CDs), were synthesized at relatively low temperature from lactose following an easy and inexpensive procedure. Modification of their surface was done by functionalization with mercaptosuccinic acid (MSA) (CDs–MSA). Transmission electron microscopy images showed regular spherical nanoparticles of 5 nm diameter. Raw and functionalized (CDs–MSA) CDs were highly fluorescent at 448 and 472 nm, with relative high quantum yield (Φ = 0.21 and 0.46 respectively). At the maximum fluorescence of CDs–MSA the intensity was quenched by addition of Ag+ ions by a static mechanism with a Stern–Volmer constant of 3.7 × 103 M−1. The analysis of the emission spectra showed that the CD–MSA complex was stable after this process. The quenching profiles showed that only 44% of the CD–MSA fluorophores are accessible to Ag+. The main figures of merit were detection and quantification limits of 385.8 nM and 1.2 μM respectively, and the precision as relative standard deviation was 1.76%. No interference was observed when other metal ions were present indicating a high selectivity for Ag+ detection. The results showed that CDs–MSA can be used for efficient quantification of Ag+ in silver nanoparticle dissolution.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...