Bond strength dependent superionic phase transformation in the solid solution series Cu2ZnGeSe4−xSx
Abstract
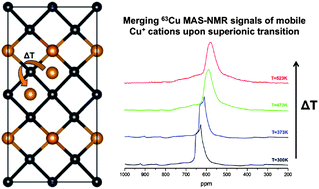
Recently, copper selenides have shown to be promising thermoelectric materials due to their possible superionic character resulting from mobile copper cations. Inspired by this recent development in the class of quaternary copper selenides we have focused on the structure-to-property relationships in the solid solution series Cu2ZnGeSe4−xSx. The material exhibits an insulator-to-metal transition at higher temperatures, with a transition temperature dependent on the sulfur content. However, the lattice parameters show linear thermal expansion at elevated temperatures only and therefore no indication of a structural phase transformation. 63Cu nuclear magnetic resonance shows clear indications of Cu located on at least two distinct sites, which eventually merge into one (apparent) site above the phase transformation. In this manuscript the temperature dependent lattice parameters and electronic properties of the solid solution Cu2ZnGeSe4−xSx are reported in combination with 63Cu NMR, and an attempt will be made to relate the nature of the electronic phase transformation to a superionic phase transformation and a changing covalent character of the lattice upon anion substitution in this class of materials.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...