Equilibrium phases of one-patch colloids with short-range attractions
Abstract
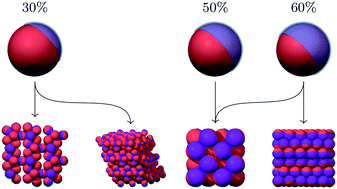
Inspired by experimental studies of short-ranged attractive patchy particles, we study with computer simulations the phase behavior and the crystalline structures of one-patch colloids with an interaction range equal to 5% of the particle diameter. In particular, we study the effects of the patch surface coverage fraction, defined as the ratio between the attractive and the total surface of a particle. Using free-energy calculations and thermodynamic integration schemes, we evaluate the equilibrium phase diagrams for particles with patch coverage fractions of 30%, 50% and 60%. For a 60% surface coverage fraction, we observe stable lamellar crystals consisting of stacked bilayers that directly coexist with a low density fluid. Inside the coexistence region, we observe the formation of lamellar structures also in direct NVT simulations, indicating that the barrier of formation is low and experimental realization is feasible. For sufficiently strong interactions, these structures spontaneously assemble from the fluid in simulations, suggesting that they might also easily form in experimental systems. In the Janus case, i.e. at 50% surface coverage fraction, no lamellar structures are formed, and the stable crystals are similar to those that have been found previously for a longer interaction range (i.e. 20% of the particle diameter). At 30% coverage fraction, we identify novel ‘open’ crystal structures with large unit cells of up to 14 particles that are stable in the strong interaction limit.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...