Influence of polarization-tilt coupling on the ferroelectric properties of smectic gels†
Abstract
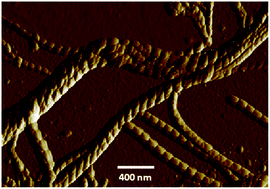
We have studied composites of a ferroelectric liquid crystal mixture with a simple organic gelating agent, employing structural, thermal, electrical and mechanical probes, investigating the influence of the coupling between the polarization and the tilt angle on the ferroelectric properties of smectic gels. The calorimetric data, presenting clear signatures of the gelation occurring in the smectic A (SmA) phase or the isotropic phase, depending on the concentration of the gelator, help in constructing a rich diagram in the temperature–gelator concentration phase space. The atomic force microscopy imaging brings out the interesting feature of the transfer of chirality from the ferroelectric liquid crystal (FLC) to the gel strands, as exemplified by the creation of nanorope structures which have attracted much attention in recent times. The influence of gelation on the magnitude of the tilt angle appears to be dependent on the probe employed: there is no change in the values obtained by X-ray diffraction, which looks at the projection of the entire molecular length onto the layer normal. In contrast, the value from the electro-optic method, wherein the molecular-core is responsible for the results, diminishes with gelator concentration. The latter feature is copied by the magnitude of the polarization also. Dielectric spectroscopy shows that gelation weakly influences the soft mode in the SmA phase. However, the Goldstone mode behaviour is strongly dependent on the gelator concentration, with the appearance of two modes in the smectic C* (SmC*) phase of higher gel concentrations. With information obtained upon application of DC bias, the origin of the two relaxations is discussed. These data are analyzed in terms of the predictions of the Landau model proposed for the ordinary (non-gel) SmA–SmC* transition showing that the gel network enhances the linear polarization-tilt coupling over the biquadratic one. Upon gelation the system becomes mechanically strong with a large increase in the elastic moduli.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...