Boundary conditions for soft glassy flows: slippage and surface fluidization
Abstract
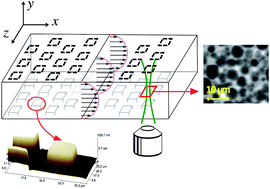
We explore the question of surface boundary conditions for the flow of a dense emulsion. We make use of microlithographic tools to create surfaces with well controlled roughness patterns and measure using dynamic confocal microscopy both the slip velocity and the shear rate close to the wall, which we relate to the notion of surface fluidization. Both slippage and wall fluidization depend non-monotonously on the roughness. We interpret this behavior within a simple model in terms of the building of a stratified layer and the activation of plastic events by the surface roughness.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...