Influence of interfacial rheology on drainage from curved surfaces†
Abstract
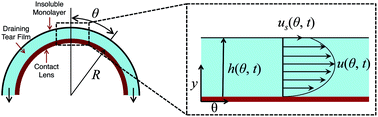
Thin lubrication flows accompanying drainage from curved surfaces surround us (e.g., the drainage of the tear film on our eyes). These draining aqueous layers are normally covered with surface-active molecules that render the free surface viscoelastic. The non-Newtonian character of these surfaces fundamentally alters the dynamics of drainage. We show that increased film stability during drainage can occur as a consequence of enhanced surface rheology. Increasing the surfactant layer viscosity decreases the rate of drainage; however, this retarding influence is most pronounced when the insoluble surfactant layer has significant elasticity. We also present a simple theoretical model that offers qualitative support to our experimental findings.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...