Dynamics of various polymer–graphene interfacial systems through atomistic molecular dynamics simulations
Abstract
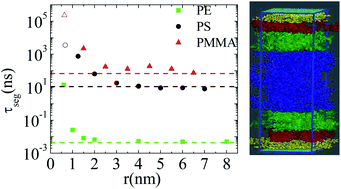
The current work refers to a simulation study on hybrid polymer–graphene interfacial systems. We explore the effect of graphene on the mobility of polymers, by studying three well known and widely used polymers, polyethylene (PE), polystyrene (PS) and poly(methyl-methacrylate) (PMMA). Qualitative and quantitative differences in the dynamical properties of the polymer chains in particular at the polymer–graphene interface are detected. Results concerning both the segmental and the terminal dynamics render PE much faster than the other two polymers; PS follows, while PMMA is the slowest one. Clear spatial dynamic heterogeneity has been observed for all model systems, with different dynamical behavior of the adsorbed polymer segments. The segmental relaxation time of the polymer (τseg) as a function of the distance from graphene shows an abrupt decrease beyond the first adsorption layer for PE, as a result of its well-ordered layered structure close to graphene, though a more gradual decay is observed for PS and PMMA. The distribution of the relaxation times of adsorbed segments was also found to be broader than those of the bulk ones for all three polymer–graphene systems.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...