Plasmonic cavities derived from silver nanoparticles atop a massed silver surface for surface enhancement Raman scattering†
Abstract
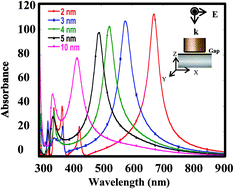
Various plasmonic cavities (PC) are formed by positioning silver nanocubes or nanospheres on a massed silver surface, being magnificently useful for surface enhancement Raman scattering (SERS) application. In this case, a red-shift in the wavelength of surface plasmon resonance (SPR) increases with the decrease in gap width according to the simulation results of absorption spectra by finite-difference time-domain method. Nanocube-insulator-metal geometry with a 2 nm gap width (2-NcIM) possesses strong electromagnetic (EM) field distribution and its PC forms near 633 nm radiation. In order to validate the simulation results, two geometries were selected for SERS experiments by using rhodamine 6G (R6G) as a model compound with 633 nm laser irradiation. To our surprise, 2-NcIM possesses respectively 2.06 × 104 and 2.41 × 104 times experimental and simulated enhancement factors (EFs) of nanosphere-insulator-metal geometry with a 2 nm gap width (1.5 ± 0.25 × 104 and 4.82 × 104), confirming the validity of the simulation results. It also prompts us to not only clarify the role of our special substrates in extra high EF for SERS application but also to design innovative, highly sensitive, and low cost substrates via the simulation results.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...