Fluid interface-mediated nanoparticle membrane as an electrochemical sensor†
Abstract
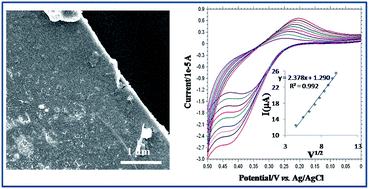
A poly(ethyleneglycol) (PEG-13)-stabilised magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticle decorated ultra-thin membrane has been devised at the water/chloroform interface by ligand cross-linking between pendant hydroxyl groups of PEG with terephthaloyl chloride. This robust nanoparticle-decorated membrane has been employed as an electrochemical sensor for the detection of L-Dopa up to nanomolar concentration.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...