Directed self-assembly of 1D microtubule nano-arrays
Abstract
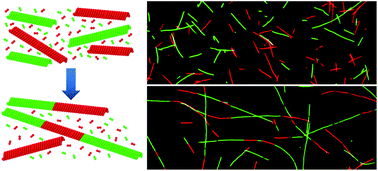
Microtubules (MTs) are biological polymer filaments that display unique polymerization dynamics, and serve as inspiration for developing synthetic nanomaterials that exhibit similar assembly-derived behaviours. Here we explore an assembly process in which extended 1D nano-arrays (NAs) are formed through the directed, head-to-tail self-assembly of MT filaments. In particular, we demonstrate that the elongation of NAs over time is due to directed self-assembly of MTs by a process that is limited by diffusion and follows second-order rate kinetics. We further described a mechanism, both experimental and through molecular dynamics simulations, where stable junctions among MT building blocks are formed by alignment and adhesion of opposing filament ends, which is followed by formation of a stable junction through the incorporation of free tubulin and the removal of lattice vacancies. The fundamental principles described in this directed self-assembly process provide a promising basis for new approaches to manufacturing complex, heterostructured nanocomposites.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...