Elucidating the endocytosis, intracellular trafficking, and exocytosis of carbon dots in neural cells†
Abstract
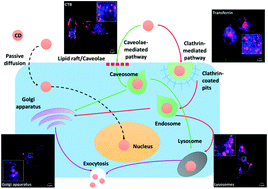
Carbon dots (CDs) due to their ultrasmall size, excellent optical properties, chemical stability, biocompatibility and most importantly possession of low toxicity have been widely used as a fluorescent probe. However, many studies on CDs are focused on their biomedical applications, the cellular behavior of CDs remains unrevealed and poorly understood. In this study, we used our recently synthesized highly photoluminescent CDs (ca. 1–5 nm) and studied their cellular uptake mechanism, intracellular distribution and exocytosis in neural cells with the help of various techniques such as confocal laser scanning microscopy, fluorescence activated cell sorter, atomic force microscopy, and transmission electron microscopy. Our results suggest that CDs exhibit low cytotoxicity and highly efficient internalization in neural cells. Cellular uptake of CDs is dose, time and partially energy-dependent along with the involvement of passive diffusion. CDs are endocytosed via caveolae-mediated and clathrin-mediated pathways. Internalized CDs are dispersed in cytoplasm and nucleus, and most of them accumulate in endo-lysosomal structures and Golgi apparatus. CDs were actively transported to the cell periphery and exocytosed with a half-life of 2 h.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...