Improved electrochemical performance of LiNi0.4Ti0.1Mn1.5O4 as cathode of lithium ion battery by carbon-coating
Abstract
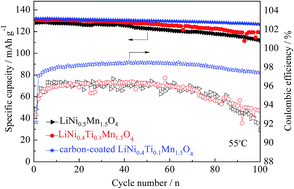
The effects of Ti substitution for Ni, carbon coating on the structure and electrochemical properties of LiMn1.5Ni0.5O4 are studied. LiMn1.5Ni0.5O4, LiNi0.4Ti0.1Mn1.5O4 and carbon-coated LiNi0.4Ti0.1Mn1.5O4 cathode materials have been synthesized by a solid-state reaction using industrial raw materials in bulk scale. X-ray diffraction clearly shows that LiMn1.5Ni0.5O4 has higher crystallinity after Ti doping. Scanning electron microscopy clearly exhibits that Ti doping does not change the basic spinel structure, as well as coated carbon layer covers the surfaces of the LiNi0.4Ti0.1Mn1.5O4 particles. In addition, charge–discharge tests indicate that LiNi0.4Ti0.1Mn1.5O4 sample has higher discharge capacities at the rates of 0.5, 1 and 3 C at 25 °C. It should be noted that carbon-coated LiNi0.4Ti0.1Mn1.5O4 shows higher discharge capacities at the rates of 5, 7 and 10 C at 25 °C as well as various rates for 55 °C. Cyclic performances developed at 25 and 55 °C demonstrate that the capacity retention is remarkably improved compared to the two uncoated samples. The influence of the Ti-doping and carbon-coating on the coulombic efficiency at high temperature (55 °C) has also been investigated. Among the various samples investigated, surface modification with carbon gives an improved coulombic efficiency. The remarkably enhanced electrochemical properties of the carbon-coated sample may be because of the suppression of the solid electrolyte interfacial (SEI) layer development and faster kinetics of both the Li+ diffusion, as well as the charge transfer reaction.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...