Structural evolution of rayon-based carbon fibers induced by doping boron†
Abstract
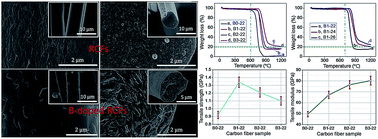
In the present work, we provide a systematic analysis of the structural evolution of rayon-based carbon fibers (RCFs) induced by doping boron using scanning electron microscope (SEM), transmission electron microscope (TEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and Raman spectroscopy. For the first time, boron-doped RCFs with tunable amounts of boron were fabricated by exposing the RCFs to a vapor of boron by the decomposition of boron carbide (B4C). SEM and XRD results indicate that at the higher temperatures the strong erosion of boron vapor not only changed the original structure of RCFs, but also produced some flaws. Interestingly, when the temperature of doping boron is higher than 2200 °C, the graphite basal planes of RCFs are perpendicular to the fiber axis. Raman spectra also confirmed the presence of disorders and flaws in graphitic layers because of the displacement and solid solution of boron in the carbon lattice. Further, the chemical environment of boron species was ascertained by 11B nuclear magnetic resonance, indicating that boron atoms exist in three chemical environments, including the substitutional boron (BC3), boron clusters and B4C. Moreover, the TGA data indicated that doping boron greatly improved the oxidation inhibition of RCFs, and is superior to increasing the heat treatment temperature for improving the oxidation resistance. Such a systematic analysis of the structural evolution and oxidation resistance of RCFs induced by doping boron thus provides industrial potential for preparing RCFs with higher oxidation resistance at up to 800 °C.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...