Molecularly imprinted TiO2 hybridized magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles for selective photocatalytic degradation and removal of estrone
Abstract
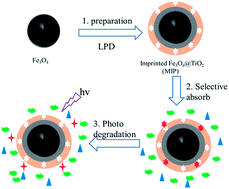
As a widely used photocatalyst, titania (TiO2) enjoys significant advantages; however, it faces the severe challenge of poor selectivity. And interestingly, molecular imprinting gains great popularity, owing to its desired recognition specificity. Herein, by using estrone as a template molecule, we prepared molecularly imprinted TiO2 hybridized magnetic ferroferric oxide (Fe3O4) nanoparticles through a semi-covalent approach by a liquid phase deposition method, for selective photocatalytic degradation and removal of target estrone with the irradiation of UV light. The obtained Fe3O4@SiO2@imprinted TiO2 displayed high adsorption capacity, fast kinetics and high selectivity. In the presence of 10 times of coexisting nontarget compounds, the apparent rate constant, kapp, for photodegradation of target estrone over the hybridized nanoparticles, was about 6 times of that over net TiO2. Also, excellent stability during long-time photocatalysis was exhibited. More importantly, the Fe3O4@imprinted TiO2 provided potential application prospectives for photocatalytic removal of trace target organic pollutants in the presence of high-level pollutants.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...