A novel CdS photocatalyst based on magnetic fly ash cenospheres as the carrier: performance and mechanism†
Abstract
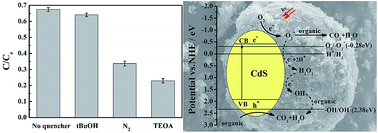
A magnetic photocatalyst was synthesized by direct growth of CdS nanoparticles on the surface of magnetic fly ash cenospheres (MFACs) through chemical deposition. The photodegradation of danofloxacin mesylate (76.2%) demonstrated that CdS/MFACs exhibited higher photocatalytic activity than that of pure CdS (71.5%) under visible light irradiation. Moreover, the as-prepared photocatalyst was relatively stable and displayed good reusability after 5 cycles. A reasonable photocatalytic mechanism for CdS/MFACs was verified by reactive species trapping, and further confirmed by ESR and a radical scavenging species, DMPO. Furthermore, qualitative hydroxyl radical analysis showed that ˙OH was present during the photocatalytic degradation process and was only generated from the photogenerated electrons in the conduction band of CdS/MFACs. In addition, the experimental results showed that the photodegradation of danofloxacin mesylate is associated with ˙O2− and photogenerated holes. Finally, the photocatalysis degradation reaction kinetics and the mechanism of photodegradation of danofloxacin mesylate were also discussed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...