Novel nanocomposites of graphene oxide reinforced poly (3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)-block-poly (ethylene glycol) and polyvinylidene fluoride for embedded capacitor applications
Abstract
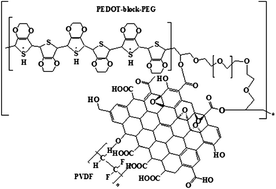
The fabrication and characterization of nanocomposites consisting of graphene oxide (GO) reinforced poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)-block-poly (ethylene glycol) (PEDOT-block-PEG)/polyvinylidenefluoride (PVDF) were investigated. The characterization of the nanocomposites was carried out using UV-vis spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction (XRD), Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC), Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) and FT-Raman spectroscopy. Dielectric properties were investigated using an impedance analyzer as a function of frequency (50 Hz to 35 MHz) and temperature in the range 40–150 °C. Atomic force microscopy (AFM) was employed to study the surface morphology of the nanocomposites. Atomic force microscopy reveals that the surface roughness increases as a function of GO loading. The presence of high surface area GO within the polymer matrix resulted in substantially improved thermal stability. Better dispersion resulted in an increase in the dielectric constant from 58.684 for 0.5 wt% to 266.091 for 3 wt% GO loading and dielectric loss from 1.758 for 0.5 wt% GO to 17.694 for 3 wt% GO. High values of dielectric constant are obtained with comparatively low dielectric loss. Hence, polymer nanocomposites with high dielectric constant and low dielectric loss have the potential to be used in the electronics and electric industry.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...