Sanguinarine, a promising anticancer therapeutic: photochemical and nucleic acid binding properties
Abstract
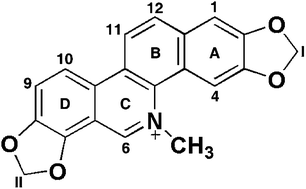
Sanguinarine is a benzophenanthridine plant alkaloid with remarkable therapeutic utility. It undergoes photochemical changes and also forms strong complexes with nucleic acids, the latter being considered to be one of the important determinant for its therapeutic action, particularly the anticancer activity. This review highlights the photochemical aspects of sanguinarine and its binding properties to various structural forms of DNA and RNA as reported from a variety of physicochemical and calorimetric studies. These properties may serve as guiding factors for the development of sanguinarine as a therapeutic agent.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...