Improvement of boehmite nanoparticles' aqueous dispersability by controlling their size, shape and crystallinity†
Abstract
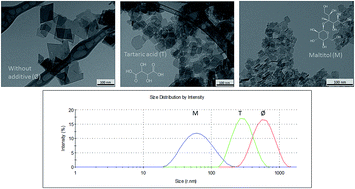
In this work, results on the control of size, shape, crystallinity and aqueous dispersability of boehmite prepared by a hydrothermal process are reported. The two step synthetic procedure entailed the precipitation of a xerogel by adding NaOH until pH 10 to a solution of aluminum nitrate at 100 °C without or with additives such as tartaric acid and maltitol, and a subsequent hydrothermal treatment at 150 and 200 °C for different periods of time. The final materials were characterized by transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and elemental analysis. The stability and other characteristics of the boehmite nanoparticle aqueous dispersions were determined by measuring the zeta potential (ζ), and the particle size distribution (PSD) by dynamic light scattering (DLS). Additive-free boehmite hydrothermally processed at 150 °C for 24 h displayed average lengths of around 20 nm. On increasing the temperature to 200 °C and the holding time up to 168 h, both the particle length increased (ca. 95 nm) and the particle size distribution widened. Comparatively, the growth of the boehmite nanoparticles in the samples prepared with additives was severely restricted up to 20% of the length of additive-free obtained particles, leading to narrower particle size distributions. Modifications in their shape were also allowed. Interestingly, improved aqueous dispersion stabilities were observed for samples prepared in the presence of an additive. A higher dispersability over a wide pH window was found in maltitol-grafted boehmite nanoparticle dispersions with hydrodynamic sizes closer to the single-particle sizes, as observed by TEM. The different formation and stabilization mechanisms of the boehmite nanoparticles obtained in the presence of additives through the synthetic procedure are also discussed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...