Inertia-activated cell sorting of immune-specifically labeled cells in a microfluidic device†
Abstract
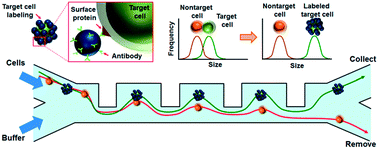
This paper demonstrates an inertia-activated cell sorting method to separate cells based on their surface protein expression by using inertial microfluidics. Target cells are immune-specifically reacted with antibody-coated microbeads and then separated from nontarget cells. As a proof of concept, separation of MCF-7 breast cancer cells from U937 lymphoma cells was achieved with 97.6% target cell recovery rate, 95% nontarget cell rejection ratio, 73.8% purity, and an enrichment ratio of 93 at a total flow rate of 8.75 mL h−1 without using any external forces.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...