Highly specific DNA detection from massive background nucleic acids based on rolling circle amplification of target dsDNA†
Abstract
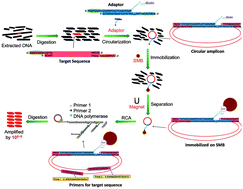
An advanced rolling circle amplification (RCA) strategy based on the target-circularization of the targeted double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) was established. Different from the traditional padlock-RCA, in which single-stranded probe DNA was circularized and amplified as signal amplification, our new approach could amplify a double-stranded DNA target. This special circularization of the target was realized by the ligation of target DNA with a biotin-labelled duplex adaptor containing 9 nt sticky ends by complementary base pairing. High specificity was obtained using two primers targeting the target sequence but not the probe itself in traditional padlock-RCA. With the help of streptavidin magnetic beads that immobilized the ligated dsDNA amplicon, the background nucleic acids contributing the most to non-specific amplification were eliminated. Under optimized conditions, less than 60 copies of the target sequence could be detected in the presence of massive background nucleic acids (>1012 copies of unrelated sequences). The sensitivity and specificity can rival canonical PCR. Without thermal cycles, the reduced handling and simpler equipment requirements render this assay a simple and rapid alternative to conventional methods. Based on these advantages, this method is a promising candidate in practical applications such as detecting contaminated food-borne pathogens in comprehensive food samples.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...