Improved cycling performance of a silicon anode for lithium ion batteries using carbon nanocoils
Abstract
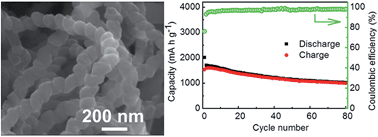
We demonstrate a new kind of silicon (Si)-based anode architecture consisting of Si nanoparticles and carbon nanocoils (CNCs). In such a hybrid structure, the conductive three-dimensional interpenetrating network of the CNCs can enhance the structural integrity of the electrode. Also, the CNCs afford a conductive network of lithium ion and electron pathways in the hybrids, thereby enabling efficient transport of electrons and the diffusion of lithium ions upon charging–discharging process. As a result, the hybrids exhibit much-improved cycling performance.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...