Immobilization of iron hydroxide/oxide on reduced graphene oxide: peroxidase-like activity and selective detection of sulfide ions†
Abstract
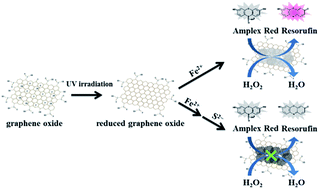
We prepared nanocomposites of amorphous iron hydroxide/oxide immobilized on reduced graphene oxide (FeOxH–rGO) with peroxidase-like activity for the detection of sulfide (S2−) ions. FeOxH–rGO nanocomposites were prepared by reaction of GO (size ∼ 300 nm) partially reduced by ultraviolet irradiation with Fe2+ in Tris–borate solution (5.0 mM, pH 7.0). The amorphous FeO(OH) and Fe(OH)2 were immobilized on rGO to form FeOxH–rGO nanocomposites. The as-prepared FeOxH–rGO nanocomposites exhibited peroxidase-like catalytic activity in the H2O2-mediated oxidation of Amplex Red (AR) to fluorescent resorufin. Our AR/FeOxH–rGO probe allowed the detection of H2O2 down to 50 nM within 10 min under microwave irradiation (170 W). The catalytic activity of FeOxH–rGO was significantly suppressed in the presence of S2− because of the formation of FeS on the FeOxH–rGO nanocomposites' surfaces. The H2O2/AR–FeOxH–rGO probe provided a limit of detection (signal-to-noise ratio = 3) of 50 nM for S2− with high selectivity (>100-fold) with respect to other anions. Taking advantage of their high stability and selectivity, we employed our H2O2/AR–FeOxH–rGO probe for the detection of S2− in hot spring samples (75.1–619.5 μM) and the results showed good correlation (r = 0.98) with results from inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. This label-free, rapid, and simple sensing system shows great potential for the detection of S2− ions in real samples.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...