A new strategy for fluorometric detection of ascorbic acid based on hydrolysis and redox reaction†
Abstract
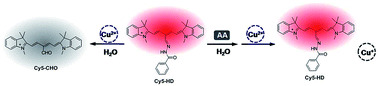
In this study, a near-infrared, indole-cyanine probe, i.e. Cy5-HD, was designed for the detection of ascorbic acid for the first time. The probe has a hydrazone moiety that can be hydrolyzed by Cu2+ to induce the fluorescence quenching of Cy5-HD. However, the fluorescence quenching ability of Cu2+ will be weakened or even disabled in the presence of ascorbic acid, thus the fluorescence recovers. The practical applicability of Cy5-HD was tested by the determination of ascorbic acid in human urine samples, and satisfactory results were obtained.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...