The role of F-dopants in adsorption of gases on anatase TiO2 (001) surface: a first-principles study
Abstract
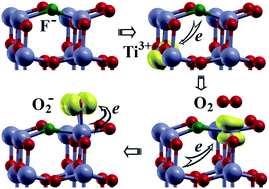
We performed a systematic investigation of adsorption of small gas molecules (O2, CO, NO, NO2 and SO2) on pristine and fluorine doped (F-doped) anatase TiO2 (001) surface using density functional theory (DFT). Three kinds of F-dopants, which were achieved by substituting a surface O2C atom (FI), or a surface O3C (FII), or an O3C atom below a surface Ti5C with an F atom (FIII), were studied to investigate the effects on the surface properties as well as the adsorption of molecules. The influence of F-dopants on the adsorption energy, charge transfer and magnetic moment of the most stable adsorption configurations of these molecules on the surfaces are thoroughly discussed. Three types of F-dopants were found to significantly promote the adsorption of O2, NO and NO2. However, the promotive effect of FI and FII dopants was not found upon the adsorption of CO and SO2. Only the FIII dopant was found to have a promotive effect on the two molecules. The mechanisms of interactions between molecules and surfaces are examined by analyzing their electronic structure and charge transfer. The results show that Ti3+ induced by F-dopants plays an important role in enhancing the interaction between gas molecules and TiO2 surfaces.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...