In vitro gene expression and preliminary in vivo studies of temperature-dependent titania–graphene nanocomposites for bone replacement applications
Abstract
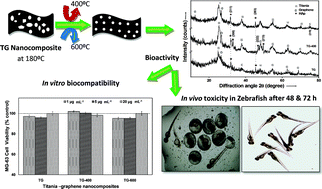
To meet the demand for biomaterials due to increasing bone defects and damage, we sought to synthesize titania–graphene nanocomposites at different sintering temperatures and then optimize them to explore their potential applications in biomaterials. The nanocomposites with higher surface area (212.85 to 233.87 m2 g−1) and mechanical strength ranging from 0.430 to 2.11 GPa were subjected to 1.5 mM simulated body fluid to confirm their bioactivity mechanisms. The non-significant toxic nature of nanocomposites in MG-63 osteoblast cell lines and controlled swelling and degradation rates indicate the suitability of these materials for biomedical applications. Moreover, the obtained percentage of mitochondrial damage, osteocalcin, osteopontin and collagen type I gene expression level in MG-63 cell line confirms that the nanocomposite sintered at 400 °C is the more optimal biomimetic material among the prepared nanocomposites. The preliminary in vivo toxicity of the nanocomposite sintered at 400 °C in zebrafish (Danio rerio) shows a non-toxic nature. These optimization studies will help further research and optimization of promising biomimetic materials for the repair and reconstruction of natural bone tissue.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...