Plasmon-induced decarboxylation of mercaptobenzoic acid on nanoparticle film monitored by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy†
Abstract
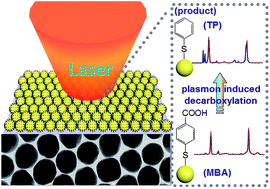
Surface plasmon plays an important role in surface catalysis reactions, and thus the tuning of plasmon on metal nanostructures and the extension of plasmon induced surface catalysis reactions have become important issues. Au nanoparticle monolayer film was fabricated by the assembling of Au nanoparticles at the liquid–air interface with numerous “hot spots” for strong surface plasmon coupling. A facile approach was developed to achieve the decarboxylation reaction driven by appropriate surface plasmon on the Au nanoparticle monolayer film surface, and surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) has been developed as a sensitive tool for the in situ monitoring of the plasmon induced surface reaction. The effects of the power and wavelength of the laser and solution pH on the decarboxylation reaction were investigated. With laser illumination, para-mercaptobenzoic acid (PMBA) was transformed to thiophenol (TP), and the decarboxylation was enhanced on increasing the laser power and illumination time. The results revealed that the carboxylate groups of the adsorbed PMBA molecules were removed to produce TP, which were still adsorbed onto Au surfaces. The solution pH values exhibited a significant influence on the decarboxylation reaction. In air and neutral solution, decarboxylation proceeded at a slow rate to transform PMBA to TP, while it was absent in acidic solution. The deprotonated carboxylate group accelerated the decarboxylation for producing TP with a fast rate in alkaline solution. As a comparison, a similar plasmon driven decarboxylation reaction was observed on a Ag nanoparticle monolayer film surface. These results suggested that the transformation from PMBA to TP molecules on an Au nanoparticle film surface under laser illumination was associated with a surface-catalyzed reaction driven by local surface plasmon.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...