Dye adsorbed on copolymer, possible specific sorbent for metal ions removal†
Abstract
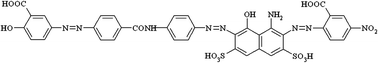
The efficiency of styrene-divinylbenzene functionalized with trimethylamonium groups as sorbent for the direct dye removal from aqueous solutions was investigated. The influence of process variables such as initial concentration, temperature and pH was developed. The amount of adsorbed dye was maximized at higher initial dye concentrations, while the removal percentage decreased. The increase of the temperature induced a positive effect on the adsorption indicating that the process is endothermic. The maximum removal percentage was obtained in acidic medium. The adsorption kinetics followed the pseudo-second-order equation, with regards to the intra-particle diffusion rate. The experimental data was well correlated by the Sips adsorption model, and the maximum theoretical adsorption capacity was determined to be 83.75 mg dye g−1 copolymer. The new obtained specific sorbent (dye-attached to copolymer) was investigated in the removal of heavy metals ions (Cu, Zn). Very high adsorption rates were observed at the beginning of the adsorption process and the equilibrium was achieved in about 5 minutes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...