A novel intermediate-temperature all ceramic iron–air redox battery: the effect of current density and cycle duration
Abstract
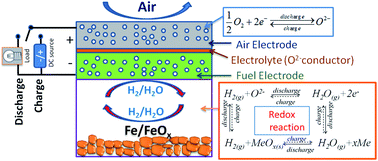
We here report the energy storage characteristics of a new all ceramic iron–air redox battery comprising of a reversible solid oxide fuel cell as the charger/discharger and a Fe–FeOx redox couple as the chemical storage bed. The effects of current density and cycle duration on specific energy and round trip efficiency of the new battery have been systematically studied at 650 °C and 550 °C. The results explicitly show that current density is the most influential variable on the performance, signifying the importance of improving electrochemical performance of the reversible solid oxide fuel cell.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...