l-(+)-Lactic acid production by co-fermentation of cellobiose and xylose without carbon catabolite repression using Enterococcus mundtii QU 25
Abstract
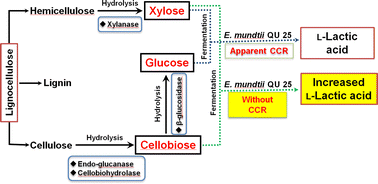
The use of lignocellulosic biomass for the production of optically pure lactic acid remains challenging because it requires efficient utilisation of mixed sugars without carbon catabolite repression (CCR). Enterococcus mundtii QU 25, a novel L-lactic acid-producing strain, was used in this study to ferment mixed sugars. This strain exhibited apparent CCR in a glucose–xylose mixture; however, replacement of glucose by cellobiose (cellobiose–xylose mixture) led to simultaneous consumption of both sugars without CCR. The production of lactic acid and activity of enzymes related to xylose metabolism were also investigated. Xylose isomerase and xylulokinase specific activity in cellobiose–xylose grown cells was three times higher than that in glucose–xylose grown cells. The addition of yeast extract and ammonium hydroxide effectively improved sugar utilisation and cell growth. Under the optimal conditions with simulated lignocellulosic hydrolysates, a high L-lactic acid concentration (up to 163 g L−1) was produced with a yield of 0.870 g g−1 and maximum productivity of 7.21 g L−1 h−1 without CCR in the fed-batch fermentation. Thus, we could establish rapid and simultaneous consumption of hexose and pentose sugars by using a lactic acid bacterium strain, which significantly increased production of high-purity L-lactic acid.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...