Predicting the mixture effects of three pesticides by integrating molecular simulation with concentration addition modeling†
Abstract
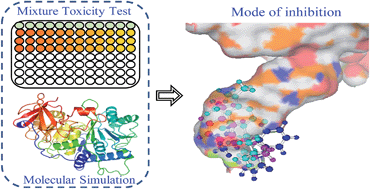
It is a tricky but fundamental problem in risk assessment to predict the combined toxicity of several chemicals by methods other than by experiment, especially for binary mixtures, in order to save time and experimental costs. Though several models have been developed, making a choice among them is difficult owing to the variation in mode of inhibition (MOI). To choose a reference model appropriately, we propose an in silico procedure which employs molecular simulation techniques to identify MOI, and which highlights the binding pattern of a small molecule to a biomacromolecule. Specifically, the method is verified by experimental study and shows that 15 binary mixtures of three pesticides, baygon, metacrate, and velpar, inhibit firefly luciferase bioluminescence. The results reveal that the pesticides share the same binding site at the bottom of the luciferin pocket, and combined toxicities could be predicted by the concentration addition model, which enables us to identify the MOI using molecular simulation techniques. In addition, there is a linear relationship between the binding free energy of the mixture (ΔGmix) calculated from the ΔGs of the components and the median effective concentrations (EC50) of the mixture.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...