A capillary electrophoresis/tandem mass spectrometry approach for the determination of monoalkyl carbonates
Abstract
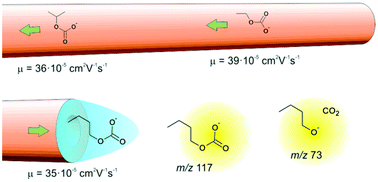
The hemiesters of carbonic acid, which include the monoalkyl carbonates (MACs), are a poorly-known class of species with potential interest for biological processes. Capillary electrophoresis (CE) with tandem mass spectrometry is herein introduced as a complementary technique to CE with capacitively coupled contactless conductivity detection (C4D) for the study of MACs. Multiple reactions monitoring mode was used to improve sensitivity and selectivity, the loss of CO2 (44 u) at low collisional energy being the key feature of the MACs. To improve the control over the temperature – and consequently over the hydrolysis of the MACs during the electrophoretic migration – a thermostating case for the silica capillary was developed. Quantitation was possible by using the estimated concentration of MAC from the initial concentrations of the reagents and the equilibrium constant in the calibration procedure. The LOD for monoethyl carbonate was 0.2 μmol L−1, which is ca. two orders of magnitude lower than the LOD obtained by CE-C4D. Using a modified BGE for the separation of MACs, the LODs for mono-3-pentyl, mono-1-butyl, mono-2-propyl, and monoethyl carbonates were 0.2, 0.5, 2, and 1.3 μmol L−1, respectively.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...