Starch-based polymer–IL composites formed by compression moulding and supercritical fluid foaming for self-supported conductive materials
Abstract
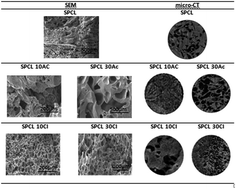
In this work, blends of starch and poly-ε-caprolactone (PCL) doped with different concentrations of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate ([BMIM]Ac) or 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride ([BMIM]Cl) were studied. The blends were characterized by mechanical analysis, infra-red spectroscopy (FTIR), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and dielectric relaxation spectroscopy (DRS), evaluating the IL doping effect. The samples were subjected to supercritical carbon dioxide foaming and the morphology of the structures was assessed. DSC shows a single glass transition and melting endotherm for foamed and unfoamed samples, having no effect upon IL doping, and DRS shows increased molecular mobility for blends with higher IL concentrations, and some hindrance for lower ones. The conductivity for SPCL doped with 30% [BMIM]Cl, before and after foaming, is comparable to the conductivity of the IL but exhibits more stable conductivity values, opening doors for applications as self-supported conductive materials.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...