N-Phenylaminomethyl hybrid silica, a better alternative to achieve reinforced PU nanocomposites†
Abstract
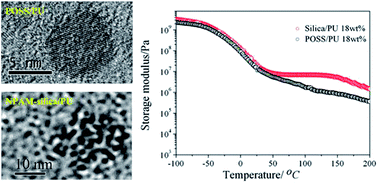
A novel N-phenylaminomethyl silica (NPAM-silica) was firstly synthesized by the one-step emulsion polymerization of N-phenylaminomethyltriethoxysilane (ND-42). The hybrid silica could be dispersed in a variety of organic solvents including THF, acetone, DMF and DMAC. The NPAM-silica was mainly composed of fully condensed silsesquioxanes and a small quantity of partially condensed silsesquioxanes, which was confirmed by 29Si NMR and MALDI-TOF MS. GPC showed that the polydispersity of the NPAM-silica was 1.08. It was then introduced into polyurethane (PU) as a chemical cross-linker. The high reactivity of NPAM-silica was investigated by means of solid state Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (SSNMR). TEM and AFM showed that the NPAM-silica was nano-dispersed in the hard segments region of PU. The mechanical properties of the NPAM-silica/PU nanocomposites in the rubber state were enhanced when NPAM-silica was added, which was reflected in the DMA and tensile tests at constant Ttest − Tg. It is also concluded that the increase of the modulus was derived from both the nanofiller contribution and entropic contribution which were tested by the temperature dependence of the modulus at the rubber region. NPAM-silica/PU possessed a higher storage modulus at the rubber plateau than that of N-phenylaminomethyl POSS/PU when the loading was below 26 wt%. The homogeneity of NPAM-silica/PU was better than that of N-phenylaminomethyl POSS/PU, which was characterized by TEM and small angle X-ray scattering (SAXS). The NPAM-silica showed greater advantages in practical applications compared with N-phenylaminomethyl POSS.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...