Adsorption of NO on ordered mesoporous carbon and its improvement by cerium†
Abstract
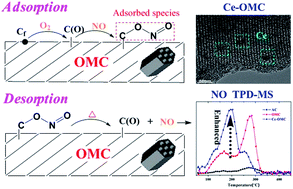
Ordered mesoporous carbon (OMC) was synthesized through a solvent evaporation-induced self-assembly method and used for NO adsorption. The structural properties, surface chemistry, and adsorption mechanism were investigated using nitrogen sorption, X-ray diffraction, transmission electron microscopy, Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, and temperature programmed desorption of CO and CO2. Results showed that the ordered mesoporous structure was synthesized and remained stable after exposure to NO and O2. The NO adsorption capacity of OMC was 16.35 mg gcat−1, which was 7.5 times that of activated carbon. This finding may be due to the large surface area of OMC and the full use of its mesopores. Characterization results showed that monodentate nitrito (–O–N![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O) was the adsorbed species, and it originated from the adsorption of NO on the oxidized C(O) sites formed by the oxidation of active free Cf sites. In addition, cerium was introduced into OMC to further improve its NO adsorption capacity to 18.61 mg gcat−1. The redox cycle between Ce4+ and Ce3+, which can provide excess adsorbed oxygen atoms to react with Cf sites and generate C(O) sites, may be responsible for the improved adsorption capacity.
O) was the adsorbed species, and it originated from the adsorption of NO on the oxidized C(O) sites formed by the oxidation of active free Cf sites. In addition, cerium was introduced into OMC to further improve its NO adsorption capacity to 18.61 mg gcat−1. The redox cycle between Ce4+ and Ce3+, which can provide excess adsorbed oxygen atoms to react with Cf sites and generate C(O) sites, may be responsible for the improved adsorption capacity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...