Novel catalyst by immobilizing a phosphotungstic acid on polymer brushes and its application in oxidative desulfurization
Abstract
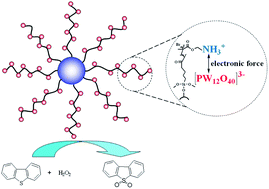
In the study, an HPW–PDMAEMA–SiO2 (phosphotungstic acid (HPW); poly-N,N-dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate (PDMAEAM)) catalyst was successfully synthesized. The synthesized HPW–PDMAEMA–SiO2 catalyst was characterized via XRD, TEM, FT-IR, TGA, and ICP-AES. The results show that the HPW active species retained its Keggin structure after immobilizing into polymer brushes. At optimal reaction conditions, the oxidative desulfurization conversion of dibenzothiophene reached 100%, and there was no significant catalytic performance decrease after six recycles. The excellent recoverability of the catalyst was attributed to the decreased leaching of the HPW active species caused by the strong interaction between the negative [PW12O40]3− ions and positive ammonium ions in the PDMAEMA polymer brushes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...